What is load balancer?
A load balancer is a device or software that distributes incoming network traffic across a group of servers or virtual machines (VMs) to ensure that no single machine becomes overwhelmed with requests. In the case of VMs, a load balancer can distribute traffic among multiple virtual machines running on a physical server, improving the performance, scalability, and availability of an application or service.
When a request comes in, the load balancer determines which VM is the best candidate to handle the request based on factors such as server load, response time, and available resources. The load balancer then forwards the request to the selected VM, which processes the request and returns the response to the client through the load balancer.
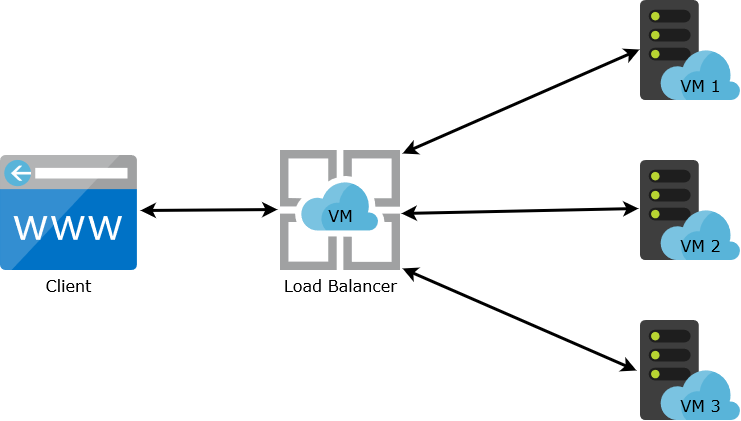
Load balancing with VMs can help to improve the performance and scalability of an application by distributing traffic across multiple VMs. This can also help to improve the availability of the application, as the load balancer can detect and redirect traffic away from failed or offline VMs to healthy ones.
Overall, load balancing with VMs is an effective way to improve the performance, scalability, and availability of an application or service by distributing traffic across multiple virtual machines.
- KVM
- Proxmox KVM
- Virtuozzo KVM
Creating a Load Balancer from Virtualizor Admin panel is very simple.
You just need to create a VM with the "Create as Load Balancer" option selected. Once the VM is created it will be created as Load Balancer.
The setting is shown below on Create VM wizard:
Once the Load Balancer is create you can see the load balancer(s) from Admin panel -> Load Balancer -> List Load Balancer